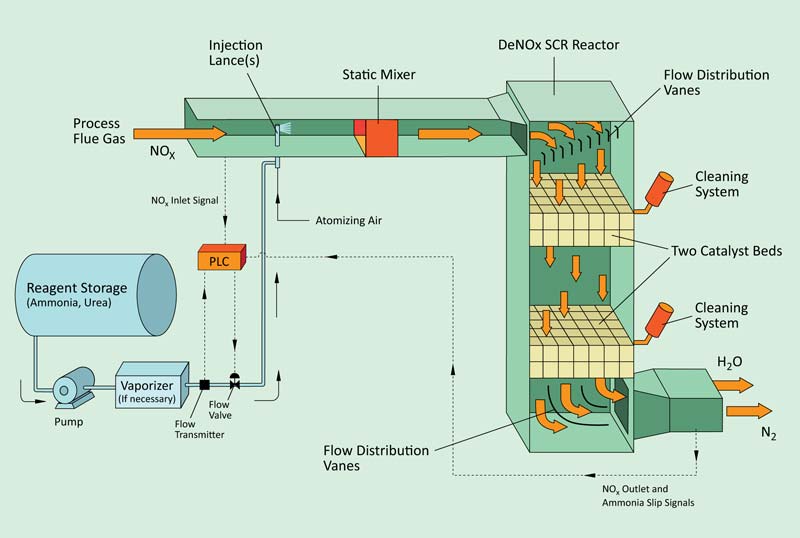
DeNOx Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) Reactors
Our deNOx SCR reactors are designed specifically to control NOx emissions on industrial applications. Our systems feature a fully integrated system design that includes modular construction, CFD modeling, a PLC-control system, a customized cleaning system, a reagent management system, and a catalyst life management system. We offer a single-source performance guarantee and equipment warranty for each reactor system.

Features
- Modular reactor housing
- Easy access to the catalyst
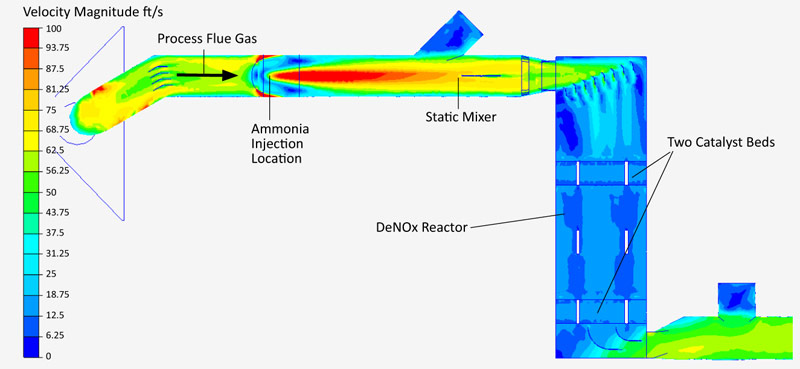
- Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) flow modeling
- Customized catalyst cleaning system
- Ammonia storage and injection systems
- Ammonia/flue gas mixing
- Catalyst life management
- PLC-based control system
- Supplemental temperature control (if needed)
The DeNOx Selective Catalytic Reduction Process
The deNOx SCR process converts NOx emissions into diatomic nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O) vapor. That is accomplished by injecting ammonia (NH3) or urea into the flue gas stream and then passing it through a catalyst bed.
Fundamental process reactions:
- 4NO + 4NH3 + O2 ⇒ 4N2 + 6H2O
- 6NO2 + 8NH3 ⇒ 7N2 + 12H2O
The Design Process and Considerations
Our sales and design engineers will review your process conditions to provide you with the best deNOx control system solution, which includes design analysis of the following:
- DeNOx removal efficiency
- Flue gas chemistry
- Operating temperature
- Catalyst selection
- Ammonia injection location
- CFD modeling and equipment layout